Mycology
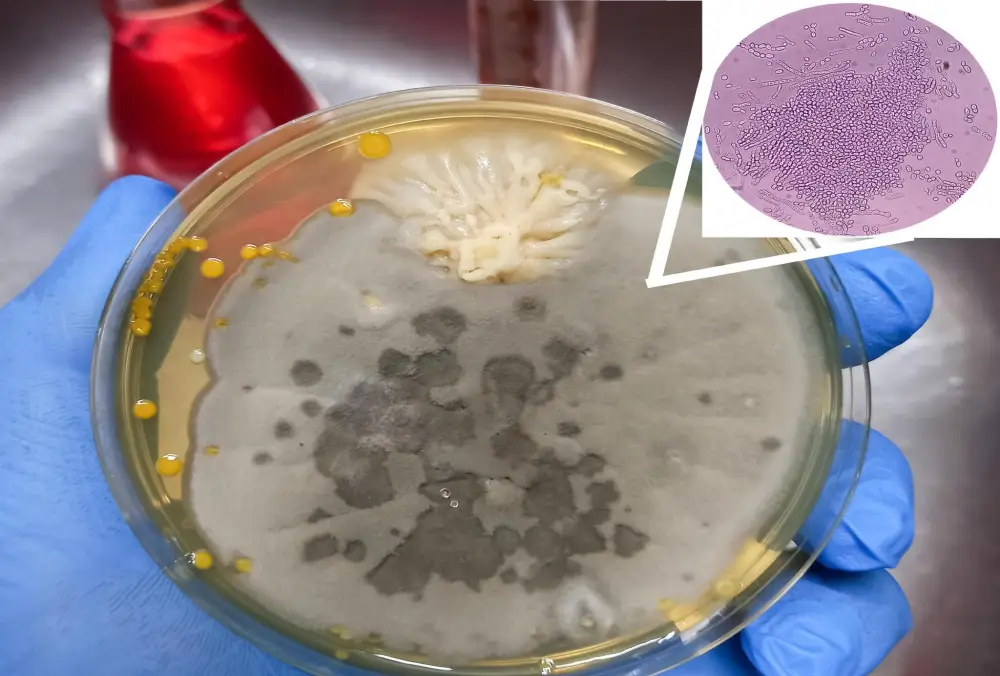
Mycology is the scientific study of fungi, a diverse group of organisms that includes mushrooms, molds, yeasts, and other related organisms. Fungi play crucial roles in various ecosystems, serving as decomposers, symbionts, and even pathogens. Here are some key aspects of mycology:
Classification of Fungi:
Mycota Divisions: Fungi are classified into several divisions, with the major ones being Zygomycota, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Glomeromycota.
Types of Fungi: The fungi kingdom comprises various forms, including mushrooms (Basidiomycota), molds (Zygomycota), sac fungi (Ascomycota), and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomeromycota).
Ecological Roles:
Decomposers: Many fungi play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter, contributing to the nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
Mycorrhizal Symbiosis: Fungi form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, known as mycorrhizae, enhancing nutrient uptake for both the fungi and plants.
Pathogens: Some fungi are pathogens that can cause diseases in plants, animals, and humans.
Medical Mycology:
Fungal Infections: Mycologists study fungal infections in humans and other animals, including diseases like candidiasis and aspergillosis.
Antifungal Drugs: Research in medical mycology contributes to the development of antifungal medications.
Research Areas:
Genetics and Molecular Biology: Understanding the genetics and molecular processes of fungi is crucial for various applications and advancements.
Biodiversity and Conservation: Mycologists explore fungal diversity and contribute to the conservation of endangered fungal species.
